Realtime UI Overview
This series walks through Realtime Kanban, a full‑stack reference app that demonstrates a Realtime UI architecture. The app behaves like a standard web application, but it’s also designed to be operated by AI agents via text or voice, and by MCP clients—including navigation and workflow automation—while keeping both front‑end and back‑end code short and easy to follow.
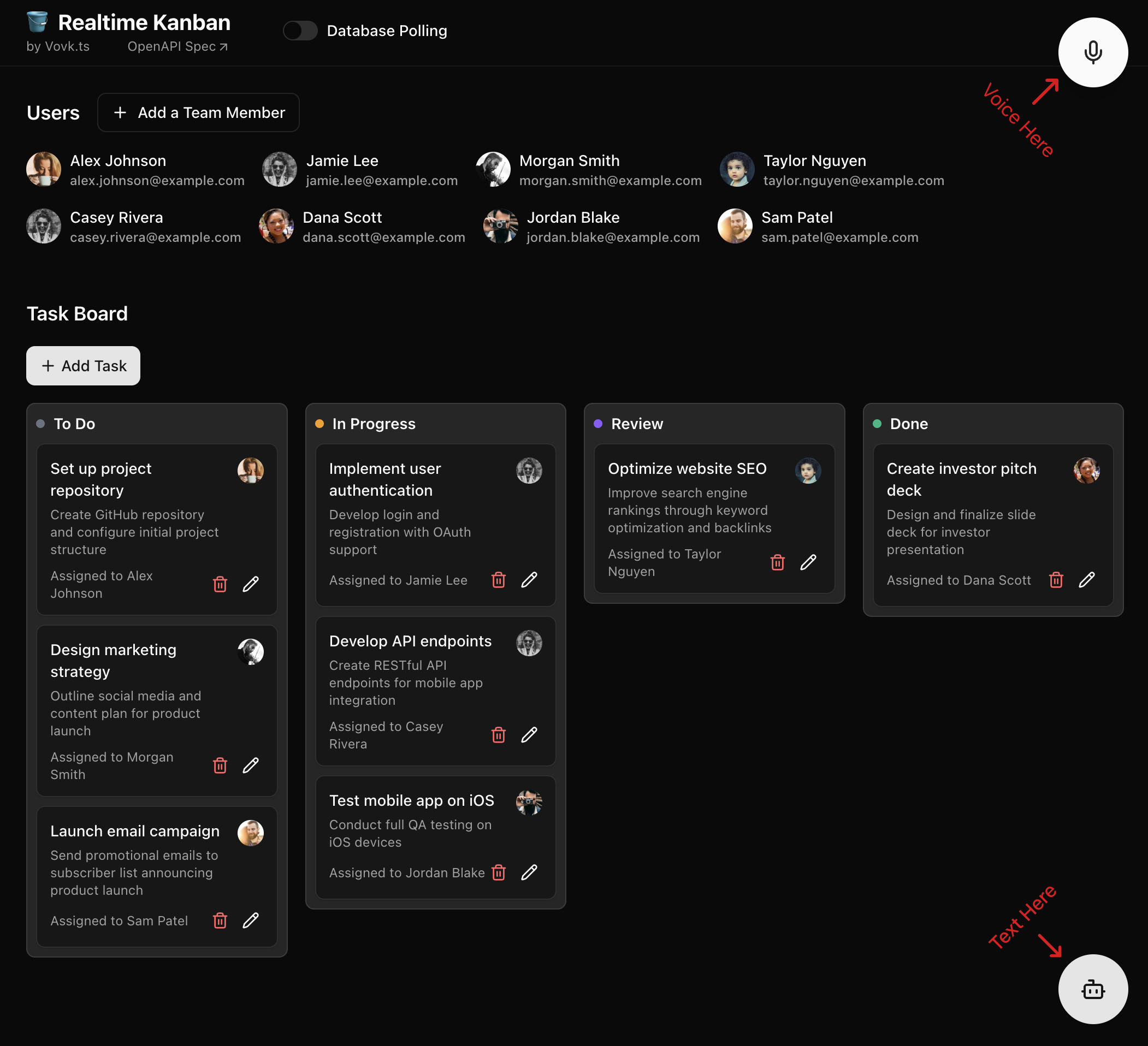
The app is intentionally minimal—just Users and Tasks—with lightweight features like password protection instead of full auth management. This makes it easy to reproduce, study, and adapt for your own projects.
Key building blocks:
- Entity-driven state normalization (front end) with Zustand : back-end responses are parsed through an entity registry that updates a normalized store, so components can read entities by ID and re-render with minimal wiring.
- Database schema as the source of truth: Postgres + Prisma define structure and drive Zod schemas via prisma-zod-generator . The same schemas validate back-end procedure inputs to keep the codebase DRY.
- Database polling events via Redis, exposed as JSON Lines streaming endpoints: changes from users, MCP clients, or bots propagate to the UI without manual refreshes.
- Text-based AI chat using the Vercel AI SDK and AI Elements : existing controllers are reused to define AI tools, and results flow back through the entity registry pipeline.
- Voice interface with the OpenAI Realtime API + WebRTC: the agent performs authorized HTTP requests through generated RPC modules; responses update the UI through the same entity registry flow. The example also includes client-side tools for in-app navigation.
- MCP server: procedures run locally on the back end and trigger polling events, updating front-end state through the entity registry.
- External updates (Telegram bot): manage tasks through text/voice inside Telegram, showing how the same app can be controlled from multiple surfaces.
You can run the app locally with Docker Compose or deploy it to any Node.js platform (for example, Vercel).
Last updated on