Setting up MCP server
Database Polling and State Normalization are set up, so the app is ready to accept changes made by external systems. Let’s now set up the MCP server to allow MCP clients to interact with our application.
The tools, as usual, are derived from the controllers using the deriveTools function from the vovk package. For more details, see Deriving AI Tools.
import { createMcpHandler } from "mcp-handler";
import { deriveTools, ToModelOutput } from "vovk";
import z from "zod";
import UserController from "@/modules/user/UserController";
import TaskController from "@/modules/task/TaskController";
const { tools } = deriveTools({
modules: {
UserController,
TaskController,
},
toModelOutput: ToModelOutput.MCP,
onExecute: (result, { name }) => console.log(`${name} executed`, result),
onError: (e, { name }) => console.error(`Error in ${name}`, e),
});
const handler = createMcpHandler(
(server) => {
tools.forEach(({ title, name, execute, description, inputSchemas }) => {
server.registerTool(
name,
{
title,
description,
inputSchema: inputSchemas as Partial<
Record<"body" | "query" | "params", z.ZodTypeAny>
>,
},
execute,
);
});
},
{},
{ basePath: "/api" },
);
const authorizedHandler = (req: Request) => {
const { MCP_ACCESS_KEY } = process.env;
const accessKey = new URL(req.url).searchParams.get("mcp_access_key");
if (MCP_ACCESS_KEY && accessKey !== MCP_ACCESS_KEY) {
return new Response(
"Unable to authorize the MCP request: mcp_access_key query parameter is invalid",
{ status: 401 },
);
}
return handler(req);
};
export { authorizedHandler as GET, authorizedHandler as POST };The code above is fetched from GitHub repository.
For simple protection, we use the mcp_access_key query parameter to authorize requests. It’s compared against the MCP_ACCESS_KEY environment variable when that variable is set.
The MCP server is now set up at the /api/mcp endpoint and can be accessed by MCP clients via the URL http://localhost:3000/api/mcp?mcp_access_key=your_access_key (replace your_access_key with the actual key, and localhost with your server address if needed).
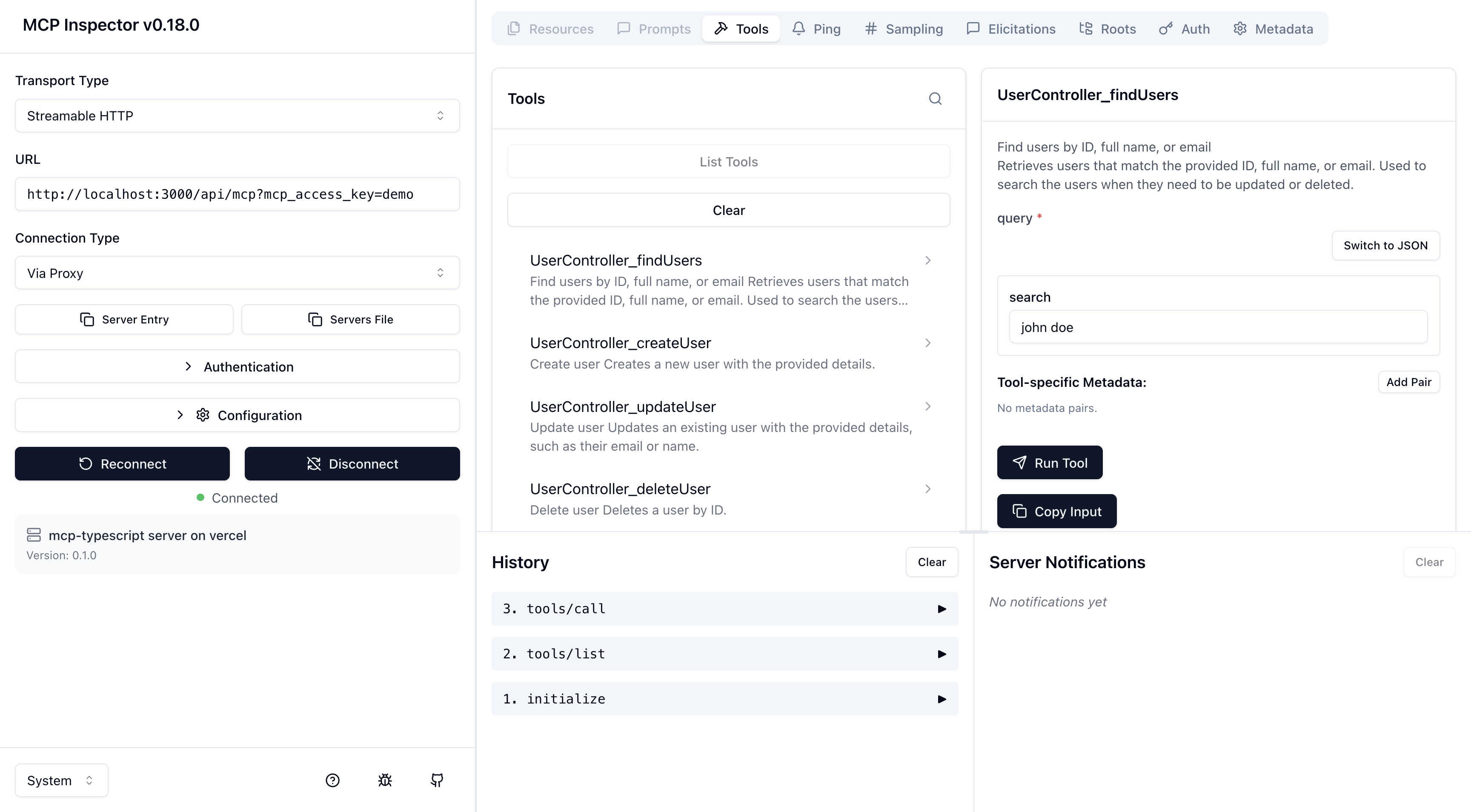
Running the MCP Inspector Locally
Run the following command to start the MCP Inspector, which allows you to interact with the MCP server we just set up. The app needs to be running locally.
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspectorUpdate the server configuration in the Inspector, select a tool, and run it to see the results.